近日,我组李闵闵博士和熊雨婷博士(生物分离与界面分子机制创新特区研究组,18T7)在蛋白质磷酸化研究方面取得新进展,开发出一种智能聚合物功能化的仿生离子通道器件,实现了酪氨酸磷酸化的实时感知与测量,并在酪氨酸激酶抑制剂筛选中展现出很好的应用潜力。
蛋白酪氨酸磷酸化是一种关键的细胞活动调节机制,异常的酪氨酸磷酸化与多种癌症密切相关。在过去的20年间,针对酪氨酸磷酸化相关激酶抑制剂药物的研究取得了长足的进展,已成为相关癌症治疗的特效药。在美国食品药品监督局批准的40余种抗肿瘤药物中,30多种是针对酪氨酸激酶的抑制剂。目前,在激酶抑制剂的筛选中,最常用手段是利用放射性同位素标记的 32P-γ-ATP作为底物,然后检测磷酸化反应产物的放射性,但该方法存在放射性污染、且需要费时的膜过滤操作。另外,基于磷酸化特异性抗体的方法(例如酶联免疫吸附测定法)也被用来检测蛋白磷酸化,然而高昂的抗体成本以及繁琐的清洗分离仍然限制了其广泛应用。近年来,一些利用光学探针标记底物的方法,能够实现高灵敏的磷酸化检测,却受限于复杂的化学标记过程。因此,一种简单、高效、低成本、免标记检测酪氨酸磷酸化、且能用于激酶抑制剂筛选的方法,显得十分重要。
通过模仿蛋白质中精氨酸与酪氨酸磷酸盐残基的相互作用,设计了含多胍基的智能聚合物,并将其修饰到锥形纳米孔道内,制备出一种功能离子通道器件。其中,聚合物依托胍基识别磷酸化肽的磷酸化残基,并且能将这种分子层面的识别作用放大到聚合物构象的变化上,并进一步被转换为通道离子电流的“OFF-ON”变化,实现对磷酸化肽的精确检测。当引入钙离子作为磷酸盐的一个竞争性结合成分时,该离子通道通过简单的纳流控逻辑门运算,即可大幅度提高对酪氨酸磷酸化肽检测的选择性。借助于对磷酸化肽的识别,该离子通道器件能够用于实时监测酪氨酸激酶催化下的酪氨酸磷酸化反应,并且在监测模型抑制剂对酪氨酸激酶活性的抑制实验中,进一步展现了这一新方法用于激酶抑制剂筛选中的潜力。
相关成果发表在《美国化学会志》(J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, DOI: 10.1021/jacs.0c06510)上。以上研究工作得到国家自然科学基金、我所创新特区组启动基金、兴辽英才计划等项目的支持。
Functional Nanochannels for Sensing Tyrosine Phosphorylation
Minmin Li, Yuting Xiong, Wenqi Lu, Xue Wang, Yunhai Liu, Bing Na, Haijuan Qin, Mingliang Tang,Hongqiang Qin, Mingliang Ye, Xinmiao Liang,* and Guangyan Qing*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020 DOI: 10.1021/jacs.0c06510
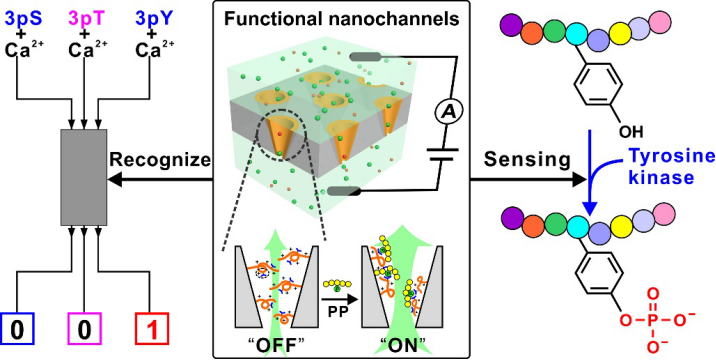
Tyrosine phosphorylation (pTyr), much of which occurred on localized multiple sites, initiates cellular signaling, governs cellular functions, and its dysregulation is implicated in many diseases, especially cancers. pTyr-specific sensing is of great significance for understanding disease states and developing targeted anticancer drugs, however, it is very challenging due to the slight difference from serine (pSer) or threonine phosphor-ylation (pThr). Here we present polyethylenimine-g-phenyl-guanidine (PEI-PG)-modified nanochannels that can address the challenge. Rich guanidinium groups enabled PEI-PG to form multiple interactions with phosphorylated residues, especially pTyr residue, which triggered the conformational change of PEI-PG. By taking advantage of the “OFF−ON” change of the ion flux arising from the conformational shrinkage of the grafted PEI-PG, the nanochannels could distinguish phosphorylated peptide (PP) from nonmodified peptide, recognize PPs with pSer, pThr, or pTyr residue and PPs with different numbers of identical residues, and importantly could sense pTyr peptides in a biosample. Benefiting from the strong interaction between the guanidinium group and the pTyr side-chain, the specific sensing of pTyr peptide was achieved by performing a simple logic operation based on PEI-PG-modified nanochannels when Ca2+was introduced as an interferent. The excellent pTyr sensing capacity makes the nanochannels available for real-time monitoring of the pTyr process by c-Abl kinase on a peptide substrate, even under complicated conditions, and the proof-of-concept study of monitoring the kinase activity demonstrates its potential in kinase inhibitor screening.