Rapid and high-efficiency discrimination of different sialic acid species using dipeptide-based fluorescent sensors
Qi Lu, Mimi Zhan, Lijing Deng, Guangyan Qing* and Taolei Sun*
Analyst, 2017, 142, 3564-3568
DOI: 10.1039/c7an00762k
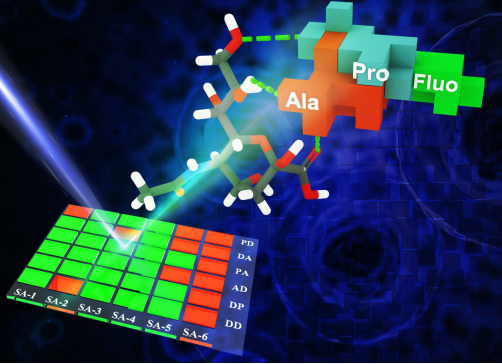
A series of dipeptide-based fluorescent sensors were developed that exhibit sensitive and distinct responses to six typical sialic acid (SA) species despite the interference of 300-fold D-glucose or other saccharides, thus contributing to a novel fluorescence sensing matrix allowing rapid and high-efficiency discrimination of different SA species. This is the first study to demonstrate that synthetic dipeptides could serve as simple but highly efficient recognition platforms for SAs. Inspired by the core binding domain [i.e., Asp-Pro-Ala-Asp (DPAD)] in a lactose-specific lectin—peanut agglutinin (PNA), six types of dipeptide combinations (DP, DA, DD, PA, PD, and AD) were designed and then labelled with fluorescein groups, generating a series of dipeptide-based fluorescent sensors. Through remarkable and distinct fluorescence quenching, these sensors exhibited unique discrimination capacity towards six representative SA species, despite the interference of 300-fold glucose. Notably, the combination of these six dipeptide sensors resulted in an efficient fluorescence detection matrix for these SAs, illustrating the significant advantage of dipeptide platforms in SA discrimination.
使用基于二肽的荧光传感器快速、高效地区分不同的唾液酸物种
开发了一系列基于二肽的荧光传感器,尽管受到300倍D-葡萄糖或其他糖类的干扰,但传感器对六种典型的唾液酸(SA)物种表现出敏感和明显的反应,从而有助于形成新型荧光传感基质,从而实现快速和高效区分不同的SA物种。这是第一个工作证明合成二肽可以作为SA的简单但高效的识别平台的研究。研究的灵感来自乳糖特异性结合凝集素—花生凝集素(PNA)中的核心结合域[即Asp-Pro-Ala-Asp (DPAD)],六种类型的二肽组合DP,DA,DD,PA,PD和设计AD,然后用荧光素基团标记,产生一系列基于二肽的荧光传感器。通过显著且独特的荧光猝灭,这些传感器对六种代表性的SA物种表现出独特的辨别能力,尽管受到300倍葡萄糖干扰。值得注意的是,这六种二肽传感器组合的荧光检测基质能高效地识别SA,说明了二肽平台在SA鉴别中的显著优势。