磷蛋白的分离对于理解其在生物学过程和病理学中的重要作用至关重要。过渡金属基受体和抗体是磷蛋白富集的常用材料,但灵敏度低,回收率低和覆盖率低。在这项工作中,通过用聚[(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺-co-4-(3-丙烯酰基硫脲基)苯甲酸)0.35](表示为PNIPAAm-co-ATBA0.35@-改性多孔硅胶),合成了新型智能共聚物修饰的二氧化硅。在ATBA单体与磷酸基团的氢键络合的驱动下,共聚物改性的表面表现出对天然a-酪蛋白(一种模型磷蛋白)的显着吸附,同时表面粘弹性和粗糙度也发生了显着变化。而且,这种吸附是可调节的,并且严格取决于载体溶剂的极性。受益于这些特征,在分散固相萃取(dSPE)模式下,使用PNIPAAm-co-ATBA0.35@SiO2可选择性富集磷蛋白。该结果显示出智能聚合物材料在磷蛋白富集方面的巨大潜力,这可能有助于自上而下的磷酸蛋白质组学研究。
Smart polymers driven by multiple and tunable hydrogen bonds for intact phosphoprotein enrichment
Xiaofei Zhang, Qi Lu, Cheng Chen, Xiuling Li,* Guangyan Qing,* Taolei Sun, and Xinmiao Liang*
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2019, 20, 858-869.
DOI: 10.1080/14686996.2019.1643259
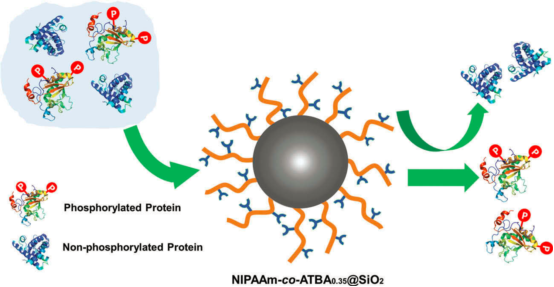
Separation of phosphoproteins is essential for understanding their vital roles in biological processes and pathology. Transition metal-based receptors and antibodies, the routinely used materials for phosphoproteins enrichment, both suffer from low sensitivity, low recovery and coverage. In this work, a novel smart copolymer material was synthesized by modifying porous silica gel with a poly[(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-4-(3-acryloylthioureido)benzoic acid)0.35] (denoted as PNIPAAm-co-ATBA0.35@SiO2). Driven by the hydrogen bonds complexation of ATBA monomers with phosphate groups, the copolymer-modified surface exhibited a remarkable adsorption toward native alpha-casein (a model phosphoprotein), accompanied with significant changes in surface viscoelasticity and roughness. Moreover, this adsorption was tunable and critically dependent on the polarity of carrier solvent. Benefiting from these features, selective enrichment of phosphoprotein was obtained using PNIPAAm-co-ATBA0.35@SiO2 under a dispersive solid-phase extraction (dSPE) mode. This result displays a good potential of smart polymeric materials in phosphoprotein enrichment, which may facilitate top-down phosphoproteomics studies.