蛋白质异常的磷酸化和糖基化与许多疾病密切相关。特别是,磷酸化和糖基化之间的相互作用调节了Tau蛋白的过度磷酸化(图A),这被认为是阿尔茨海默氏病(AD)的病理特征之一。然而,在复杂的生物样品中同时表征这两种类型的翻译后修饰(PTM)是非常具有挑战性的(图B)。由于分子间相互作用的固有局限性, TiO2和基于固定离子亲和色谱(IMAC)的富集方法因磷酸肽和糖肽的选择性低,或回收率低而受到影响(图C)。在这里,我们介绍了一种基于氢键的聚[N-异丙基丙烯酰胺-co-4-(3-丙烯酰基硫脲基)苯甲酸0.2](简称为PNI-co-ATBA0.2)作为双功能富集平台(图D),得益于ATBA捕获单元与唾液酸化聚糖末端的N-乙酰神经氨酸(Neu5Ac)的多级氢键相互作用以及共聚物链的良好的构象转变,该智能共聚物具有很高的吸附容量(370 mg/g)和高回收率(唾液酸化糖肽的回收率(从74.1%±7.0%到106%±5.0%(n = 3))。智能共聚物还具有高的富集选择性,可以从50微克HeLa细胞裂解液中,富集得到糖肽和磷酸化肽的占比为79%,从631个磷酸肽中产生721个独特的磷酸化位点,从120个糖肽中产生125个独特的糖基化位点,这将为设计PTM蛋白质组学富集材料的开发,开辟出一条新途径。
High-efficiency phosphopeptide and glycopeptide simultaneous enrichment by hydrogen bond–based bi-functional smart polymer
Qi Lu, Cheng Chen, Yuting Xiong, Guodong Li, Xiaofei Zhang, Yahui Zhang, Dongdong Wang, Zhichao Zhu, Xiuling Li,* Guangyan Qing,* Taolei Sun, and Xinmiao Liang
Anal. Chem., 2020, 92, 6269
DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b02643
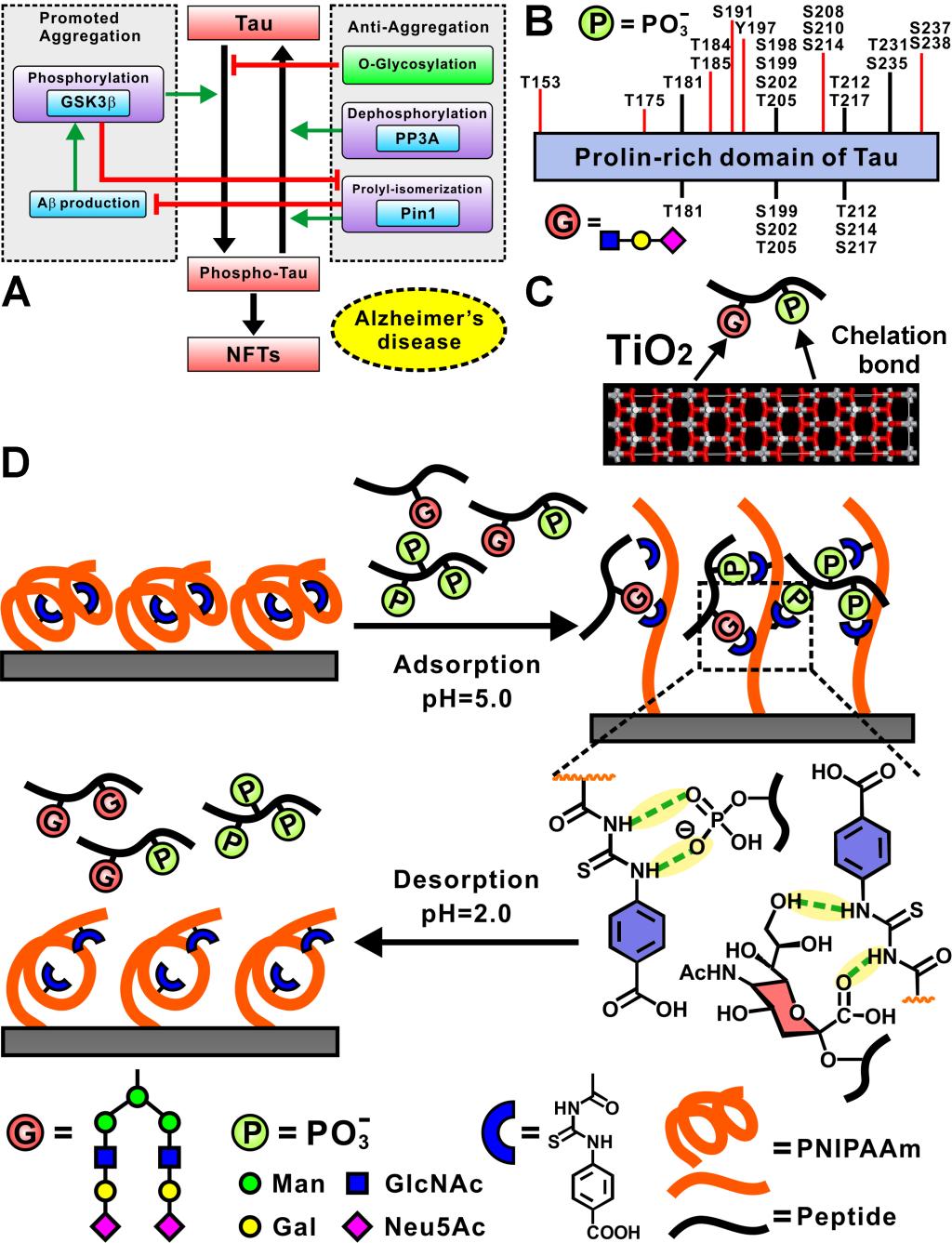
Aberrant protein phosphorylation and glycosylation are closely associated with a number of diseases. In particular, an interplay between phosphorylation and glycosylation regulates the hyperphosphorylation of protein tau, which is regarded as one of the pathologic features of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, simultaneous characterization of these two types of post-translational modifications (PTMs) in the complex biological samples is challenging. TiO2 and the immobilized ion affinity chromatography (IMAC)-based enrichment method suffers from low selectivity and/or low recovery of phosphopeptides and glycopeptides because of the inherent limitations in intermolecular interactions. Here, we introduce a hydrogen bond-based poly[(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-4-(3-acryloylthioureido)benzoic acid0.2] (referred to as PNI-co-ATBA0.2) as a bifunctional enrichment platform to solve this bottleneck problem. Benefited from multiple hydrogen bonding interactions of ATBA with N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) located at the terminals of sialylated glycans and from favorable conformational transition of the copolymer chains, the smart copolymer has high adsorption capacity (370 mg·g–1) and high recovery (ranging from 74.1%±7.0% to 106%±5.0% (n=3)) of sialylated glycopeptides. The smart copolymer also has high selectivity (79%) for simultaneous enrichment of glycopeptides and phosphopeptides from 50 mg HeLa cell lysates, yielding 721 unique phosphorylation sites from 631 phosphopeptides and 125 unique glycosylation sites from 120 glycopeptides. This study will open a new avenue and provide a novel insight for the design of enrichment materials used in PTM-proteomics.
