生物分离与界面分子机制创新特区研究组,卿光焱研究员和博士研究生杨航,系统总结了固态纳米孔在生物分子传感检测中的应用进展。
自 2001 年首次推出以来,固态纳米孔和纳米通道已经取得了巨大的成就,它们在 DNA 测序和单分子检测等生物应用中展现了巨大的潜力。纳米孔内部的密闭空间及其功能化策略为纳米孔检测提供了比任何其他检测方法更独特的优势。固态纳米孔避免了生物纳米孔的内在脆弱性,具有出色的坚固性和可制造性。然而,用于生物检测的固态纳米孔检测的灵敏度、选择性、可控性和重现性仍有待研究。科学家们在该领域的各个方面都取得了显着进展,包括制造、功能化和生物应用,以解决上述研究空白并揭示固态纳米孔在生物分子检测中的应用潜力。这篇综述描述了最先进的结果,并为读者提供了对固态纳米孔的现状和未来方向的全面见解。本综述简要介绍了过去 20 年固态纳米孔的原理和发展,然后总结了过去 5 年取得的进展。描述了各种类型的纳米孔和纳米通道的制造协议,包括基于氮化硅的孔、聚合物纳米通道和玻璃纳米吸管。此外,还讨论了赋予固态纳米孔先进物理和化学特性的附加和功能化策略。最后,展示了固态纳米孔的潜在应用,从 DNA 和药物到蛋白质和病毒。
Solid-state nanopores and nanochannels for the detection of biomolecules
Hang Yang and Guangyan Qing*
Chem. Phys. Rev. 2021, 2, 021306; https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0049078
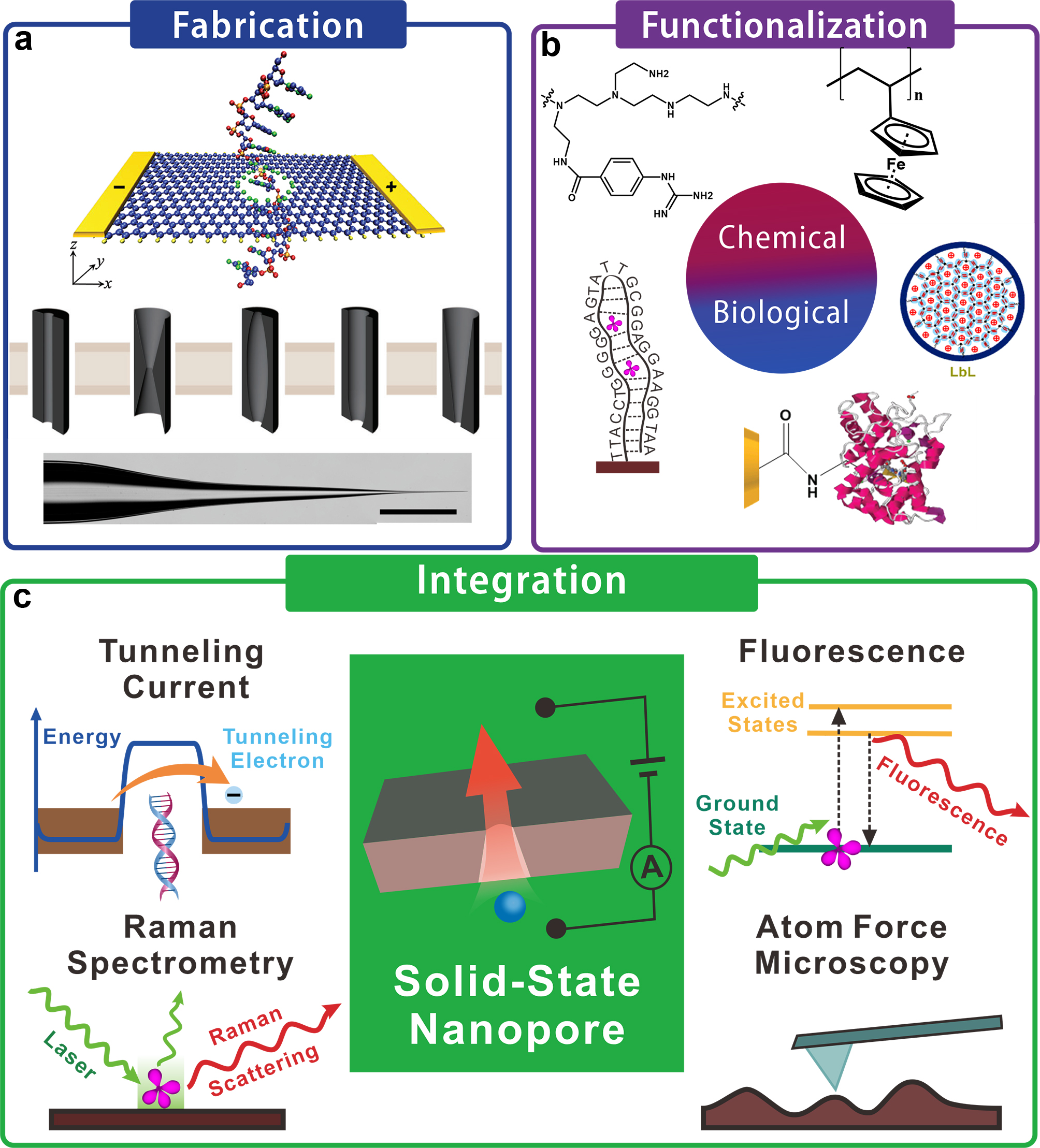
Enormous achievements have been made in solid-state nanopores and nanochannels since they were first introduced in 2001, and they have demonstrated potential in biological applications such as DNA sequencing and single-molecule detection. The confined space inside nanopores and their functionalization strategies provide nanopore detection with more unique advantages than any other detection method. Solid-state nanopores avoid the intrinsic fragility of biological nanopores and have excellent robustness and manufacturability. However, the sensitivity, selectivity, controllability, and reproducibility of solid-state nanopore detection for biological detection remain to be investigated. Scientists have made remarkable progress in all aspects of the field, including fabrication, functionalization, and biological application, to address the aforementioned research gap and to reveal the potential of solid-state nanopores’ application in biomolecule detection. This review describes the state-of-the-art results and provides readers with comprehensive insights into the current status and future directions of solid-state nanopores. This review provides a brief introduction to the principles and development of solid-state nanopores over the last two decades and then summarize the advances made over the last 5 years. Fabrication protocols of various types of nanopores and nanochannels are described, including silicon nitride-based pores, polymer nanochannels, and glass nanopipettes. Moreover, appending and functionalization strategies that confer advanced physical and chemical properties to solid-state nanopores are discussed. Finally, the potential applications of solid-state nanopores are demonstrated, from DNA and drugs to proteins and viruses.