Separation Materials Working in Both Hydrophilic and Reversed Hydrophobic Modes
Time:2022-04-27 10:20 Author:SQY
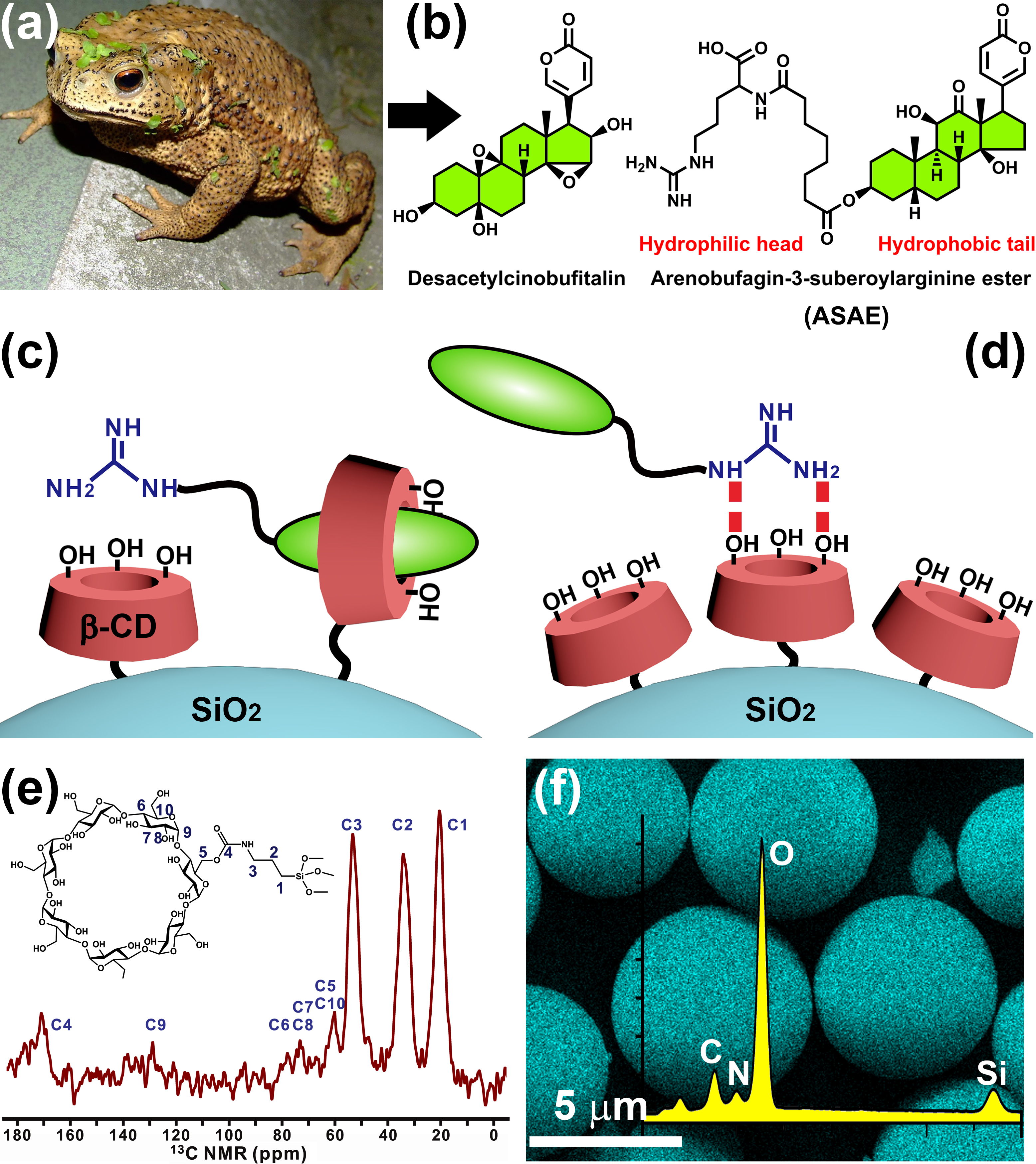
High-efficiency Two-dimensional Separation of Natural Products Based on β-Cyclodextrin Stationary Phase Working in Both Hydrophilic and Reversed Hydrophobic Modes
Qianying Sheng, Ling Wang, Leyuan Zhang, Xue Wang, Shengxu Qian, Minbo Lan,* Guangyan Qing,* Xinmiao Liang
Journal of Chromatography A 2022, 1673, 463069
Natural products are rather complex samples containing a large number of compounds ranging from polar to nonpolar, small molecules to macromolecules, as well as numerous homologs/analogs with quite similar structures, which create great opportunities and treasures for discovery of bioactive drugs. For the purpose of better understanding the complex natural products and controlling their qualities, powerful analytical techniques for adequately separating chemical constituents and tracking potentially bioactive components are quite essential. Here, a design concept of bidirectional β-cyclodextrin (β-CD)–modified chromatographic stationary phase toward separation of bufadienolides extracted from toad is proposed. Bufadienolides could be divided into two classes: toad venom ligand (AAUBs) and toad toxin (AACBs) with remarkable differences in structures and polarity. The hydrophobic cavity of β-CD can encapsulate the steroid part of AACBs while the hydroxyls exposed on the β-CD surface have strong hydrophilic interactions with the arginine part of AACBs. Isothermal titration calorimetry and hydrogen nuclear magnetic resonance titration experiment further validate the rationality of this design. Furthermore, the β-CD-based stationary phase can be used as a hydrophilic material to construct a HILIC×RPLC 2D separation mode for the separation of AACBs, also works as a reverse phase material to construct a RPLC×RPLC 2D separation mode for the separation of AAUBs with good orthogonality. This study will open an avenue and provide a novel insight for high-efficiency two-dimensional separation of natural products.